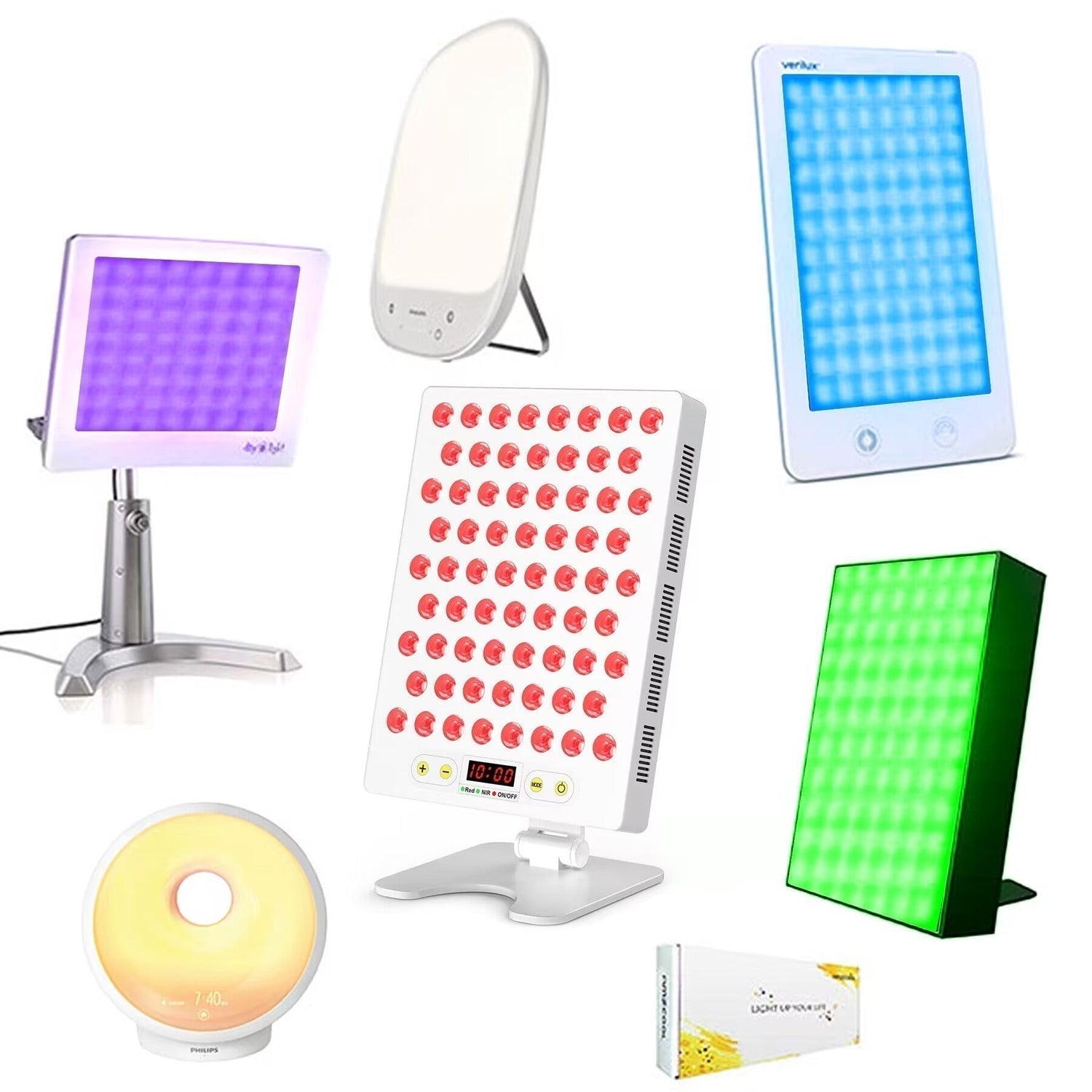
Red light therapy is used by many medical and beauty salons to emit specific wavelengths to stimulate cell growth. In addition to red LED light therapy, there are other light therapies in this non-invasive treatment, such as blue light, green light, yellow light, near infrared (NIR) light, and bright light therapy, so what's the difference between these and what do they do.
What is Red/Infrared Light Therapy?
Photobiomodulation: A combination of visible red light and invisible infrared light to help with energy support (cellular ATP production), collagen production, wound healing, pain management, and overall systemic and cellular health.
Red light falls into the visible part of the light spectrum between 630-750 nm on the electromagnetic spectrum and is readily absorbed by surface tissues and cells. For this reason, red light on its own is often used for skin health, wound healing, etc.
Since red light combined with near-infrared holds more power when used together, you’ll often find lamps and units (like this one!) offering combinations of wavelengths ranging from the red light to the near-infrared spectrum.
Near-infrared wavelengths fall into the invisible part of the light spectrum between 750 and 1400 nm, the wavelengths of light right after red visible light. Infrared light is felt at thermal energy or heat (like that emitted from a fire or incandescent light bulb).
While infrared light ranges much further (there also exists a mid-infrared and far infrared spectrum), near-infrared is the most widely studied and used infrared light spectrum.
Knowing what we know about light and wavelength length, infrared light has a longer wavelength than red visible light and can penetrate more deeply into the body, supplying beneficial light nourishment deep into our tissues, organs, and cells. Remember, approximately half of sunlight radiation itself is comprised of infrared light wavelengths!
What is the Difference Between Light Therapy, Red Light Therapy and Near Infrared Therapy?
1. Light Therapy (General Term)
Definition:
"Light therapy" is a broad umbrella term for treatments that use specific wavelengths of light to improve health, mood, or skin conditions.
Examples Include:
- Blue light therapy (for acne)
- Red light therapy (for skin repair)
- Near-infrared therapy (for deep tissue healing)
- Bright light therapy (for seasonal depression)
Think of light therapy as the category, and red/infrared therapy as specific types within that category.
2. Red Light Therapy (RLT)
Wavelength Range: ~620–660 nanometers
Key Benefits:
- Boosts collagen production for anti-aging
- Speeds up wound healing
- Reduces inflammation
- Improves skin tone and texture
Penetration Depth:
About 5–10 mm into the skin – ideal for surface-level issues like wrinkles, scars, and minor inflammation.
Common Uses:
- Anti-aging and skincare
- Hair regrowth
- Reducing redness and irritation
3. Near-Infrared Therapy (NIR)
Wavelength Range: ~800–1100 nanometers
Key Benefits:
- Reaches muscles, joints, and bones
- Enhances circulation and oxygenation
- Reduces chronic pain
- Promotes deep tissue repair
Penetration Depth:
Up to 5 cm (2 inches) – ideal for deep tissue treatments
Common Uses:
- Muscle recovery
- Joint pain relief
- Athletic performance enhancement
- Neurological support
Key Differences Summary Table
| Feature | Light Therapy | Red Light Therapy | Near-Infrared Therapy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scope | General term | A type of light therapy | A type of light therapy |
| Wavelength | Varies | ~620–660 nm | ~800–1100 nm |
| Depth of Penetration | Depends on type | Shallow (skin-deep) | Deep (muscles & joints) |
| Main Focus | Skin, mood, health | Skin repair, beauty | Pain relief, deep healing |
| Common Uses | Acne, SAD, aging | Wrinkles, scars, tone | Arthritis, recovery, pain |
Red Light vs. Near Infrared Therapy
Red light therapy and near infrared light therapy fall into a whole other light spectrum. The two are often confused as the same thing but they are really quite different. Red light falls into the visible part of the light spectrum between 630-700 nm on the electromagnetic scale and is used to treat the surface of the skin.
Near infrared wavelengths fall into the invisible part of the light spectrum between 700 and 1200 nm. So what does this mean? The longer the wavelength, the deeper the penetration to deliver energy to the cells, stimulating healing and relieving pain.
Various cell and tissue types each have their own unique light absorption methods at varying wavelengths. This means certain tissues absorb certain kinds of light. For example, light vibrating at the blue wavelength is great for skin while other colors may penetrate the skin more deeply – see LEDs in Dermatology study.
The optimal NIR technology is done by LED as you are able to control the surface temperature. Also LED disperses over a larger surface area than a RED light halogen or laser. Another major difference between LED and halogen and Laser is the way light energy is delivered (optical power output – OPD). The OPD of LED Near is measured in milliwatts and laser and halogen is measured in watts. This allows LED to have a more gentler delivery as it will not damage tissue and will not have the same risk of accidental eye injury. Also with LED NIR disperses over a greater surface area give a faster treatment time.
NASA research has found that the NIR electromagnetic frequency band of energy penetrates deeply into the body and can have a healing effect on our individual cells. For example, inside the mitochondria of every cell are receptors which respond to Near Infrared wavelengths. The light triggers an increase in cell metabolism, protein synthesis (including collagen), and anti-oxidant activity (meaning the cells detoxify). Additionally, it reduces inflammation and pain while simultaneously triggering growth and regeneration in the cells.
Light therapy affects mood, circadian rhythm and other body processes, while Near Infrared Therapy acts a pain reliever and cell rejuvenator – two VERY different forms of energy, but both beneficial.
Benefits of Near Infrared Therapy
Near Infrared Therapy falls on the spectrum of Infrared Light which is barely visible to the eye and is also the shortest infrared wavelength on the electromagnetic spectrum. Infrared typically includes wavelengths from 700 nm to 1 mm. Near Infrared light, however, falls in the spectrum of 700 nm to 2500 nm.
- Boosts metabolism
- Recharges mitochondria
- Stimulates white blood cell production
- Reduces body fat
- Promotes cell regeneration
- Increases energy
- Reduces inflammation within the body
- Improves circulation within the body
- Heals wounds faster
- Faster recovery time after working out
- Provides pain relief
- Rejuvenates the skin
- Lessens joint and muscle pain
- Improves flexibility
- Provides anti-aging benefits to your body
What is LED light therapy?
LED light therapy is a non-invasive skincare treatment that uses light-emitting diodes (LEDs) to deliver specific wavelengths of light to the skin. These lights stimulate various biological processes in the skin and underlying tissues, depending on the color (wavelength) of the light.
What does LED light therapy do?
LED light therapy helps treat a variety of skin concerns and conditions, including:
- Eczema.
- Hair loss.
- Mild to moderate acne.
- Psoriasis.
- Rough, scaly, precancerous spots on the skin (actinic keratosis).
- Rosacea.
- Sun damage.
- Wounds.
- Wrinkles.
In some cases, LED light therapy may treat small and superficial basal cell carcinoma (BCC). BCC, a skin cancer, is the most common type of cancer, affecting about 3.6 million Americans each year.
Green LED Light Therapy
Green light therapy, typically at 520 nm, is less studied but shows promise in specific applications. Researchers are testing green light therapy to see if it reduces migraine pain. Patients sit in a dark room lit only by a string of green LED lights for two hours. Some patients found immediate relief in the intensity and frequency of their migraines. Many said that other colors of light made their headaches worse, but that the green light did not. Green light may also boost serotonin levels and reduce sensitivity to input from the nerves by stimulating the body’s own opioid system.
In a comparative study of red and green LED light therapy for androgenetic alopecia, both therapies effectively enhanced hair growth, increasing density and thickness over 6 months. Red LED demonstrated superior improvements in specific measures, such as a greater increase in hair diameter. Green light therapy requires eye protection to be effective and remains an area of ongoing research.
Yellow LED Light Therapy: Addressing Redness and Photoaging
Yellow light therapy, with wavelengths around 570–590 nm, penetrates deeper than blue light and is effective for skin issues involving redness, such as rosacea. It may also reduce the effects of sun damage. In one in vitro study, yellow wavelengths were used to reduce damage from UV rays. The yellow wavelengths supported recovery from oxidative stress, reduced inflammation, and boosted collagen production. This suggests that yellow lights could be valuable in the treatment of photoaged skin and in reducing skin redness.
Like red and NIR wavelengths, yellow wavelengths stimulate cellular energy production to boost cells’ ability to perform their functions, repair themselves, and replicate, which is an important part of the healing process. Yellow light therapy is often used in combination with other wavelengths to enhance overall skin rejuvenation.
Near-Infrared (NIR) Light Therapy: Deep Tissue Benefits
Near-infrared light therapy, operating at 700–1100 nm, penetrates deeper into muscles, joints, and even bones, offering benefits beyond superficial skin enhancement. NIR light therapy prompts the body’s natural recovery process, providing relief for conditions like pain and muscle soreness. It is invisible to the human eye, distinguishing it from red light. Combining red and NIR therapies caters to a broader spectrum of concerns, working on both surface and deeper layers to elevate vitality and rejuvenation.
Infrared light therapy benefits extend to pain management and rehabilitation. Many powered infrared sources are available, including infrared heat lamps, infrared saunas, and LED arrays often combining red light and near-infrared light. For comprehensive treatment, Red Light Therapy Devices Full Body offer combined red and NIR wavelengths for enhanced therapeutic outcomes.
Bright Light Therapy: Mood and Circadian Regulation
Bright light therapy, typically using full-spectrum light at 5000–6500K and 10,000 lux, mimics natural sunlight to trigger a circadian response. It is primarily used to treat Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD) by boosting serotonin levels and slowing melatonin production, helping users feel more alert. While the most common use of bright light therapy has been for treating SAD, you don’t need a clinical diagnosis to enjoy bright light’s stimulating and awakening benefits every morning.
Unlike red or NIR therapies, bright light therapy focuses on mood and energy rather than cellular repair. It requires exposure for about 30 minutes daily, typically in the morning, and does not penetrate the skin to affect deeper tissues. Its distinct mechanism makes it complementary rather than competitive with LED-based therapies.
Comparative Efficacy and Safety
Red LED light therapy stands out for its versatility and safety profile. Compared to laser phototherapy, Light Emitting Diode Therapy (LEDT) is recognized for its enhanced safety profile, exhibiting fewer short-term and long-term side effects. This distinction stems from LEDT’s use of non-coherent light at lower intensities, which minimizes the risks of tissue damage and discomfort often associated with the high-intensity, coherent light of lasers.
Blue light therapy, while effective for acne, carries risks of free radical damage and requires careful eye protection. Green and yellow light therapies are promising but lack the extensive research backing red light. NIR therapy offers deep tissue benefits but is less focused on superficial skin concerns compared to red light. Bright light therapy serves a distinct purpose in mental health and circadian regulation, with minimal overlap in applications.
Red light therapy appears to be mostly safe when used correctly, especially in the short term. One early-stage clinical trial found that at high levels, red LED lights can cause blistering and redness on the skin. Red light therapy may also cause eye damage in some cases, so it is best to wear protective goggles when using a device. There is no evidence that red light therapy causes cancer, as it does not use ultraviolet rays.
Summarize
There are more types of red light therapy devices, such as handheld light bars to full body panels and treatment beds, which can target different parts of the body and have different light waves at the same time. For those who really need a red light therapy device to help them, it is best to choose an FDA-approved one when choosing one, so as to ensure safety and results.
FAQ
1. What is the main difference between red LED light therapy and other light therapies?
Red LED light therapy uses low-wavelength red light (620–750 nm) to penetrate the skin and stimulate cellular repair, primarily for skin rejuvenation and pain relief. Blue light targets acne-causing bacteria, green light may reduce migraines, yellow light addresses redness, NIR penetrates deeper for muscle and joint benefits, and bright light therapy regulates mood and circadian rhythms.
2. Is red LED light therapy safe for home use?
Yes, when used correctly, red LED light therapy is safe for home use. FDA-cleared devices minimize risks, but users should follow instructions, avoid overuse, and wear protective goggles to prevent eye damage. High-intensity settings may cause skin redness or blistering if not managed properly.
3. How long does it take to see results from red light therapy?
Results vary depending on the condition and device. Skin improvements, like reduced wrinkles or acne, may take 4–8 weeks of consistent use (3–5 sessions per week). Pain relief or hair growth may require similar or longer durations. In-office treatments often yield faster results due to higher intensity.
4. Can I combine different light therapies for better results?
Yes, combining therapies like red and blue light for acne or red and NIR for skin and muscle benefits is common and safe. Some devices offer multiple wavelengths for versatility. Consult a healthcare provider to tailor a treatment plan for your needs.
5. Are there any conditions where light therapy should be avoided?
Light therapy may not be suitable for individuals with photosensitivity, certain eye conditions, or those taking photosensitizing medications. Pregnant individuals should consult a doctor, as research on safety is limited. Always seek medical advice before starting any light therapy.
References:











Leave a comment
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.