Red Light Therapy Before and After Workout: The Ultimate Guide
Introduction
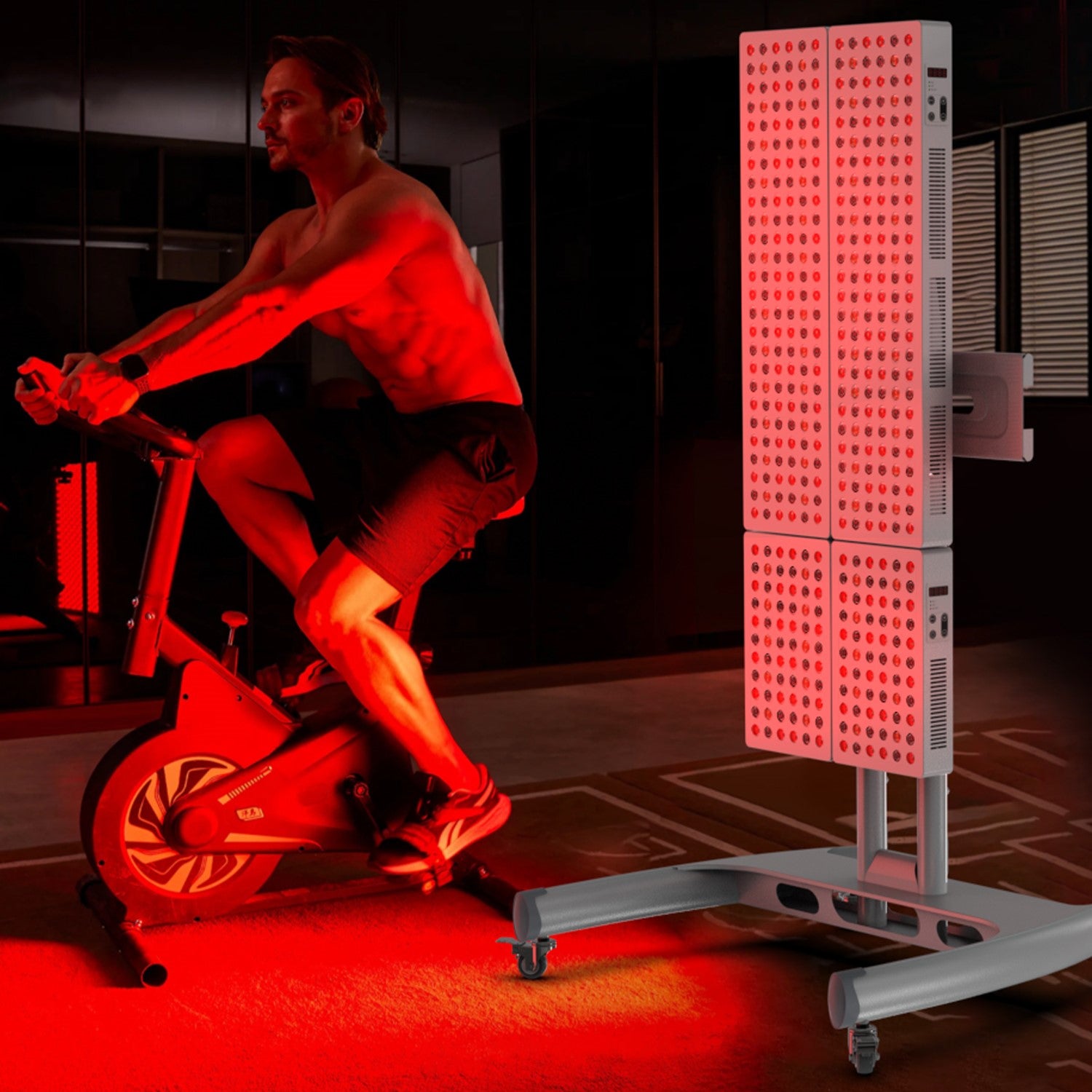
Ever wished there was a simple trick to enhance your post-workout recovery and potentially boost your gym performance? Look no further than Red Light Therapy—a revolutionary technique that has transformed the fitness world. It's like a switch that instantly soothes those achy muscles and prepares you for your next workout, faster than ever before.
Now, here's the burning question: should you incorporate Red Light Therapy before you hit the weights, or is it more effective after you've completed your workout? In this comprehensive guide, we'll delve into the what, why, and when of Red Light Therapy, providing you with all the essential information on how to seamlessly integrate it into your workout routine.
Whether you're striving to take your fitness game to the next level or seeking a reliable method to alleviate those pesky post-gym sore spots, stay tuned to discover how Red Light Therapy can become your new workout companion.
What is Red Light Therapy?
Red light therapy, also known as low-level laser therapy or photobiomodulation, is a non-invasive treatment that uses specific wavelengths of red light to promote healing, reduce pain, and enhance recovery.
Red light therapy involves exposing the body to low levels of red or near-infrared light. These wavelengths penetrate the skin and stimulate cellular energy production, leading to various therapeutic benefits. This therapy has been studied for several decades and has gained popularity in recent years due to its potential in improving overall health and wellness.
How Does Red Light Therapy Work?
Red Light Therapy works by delivering specific wavelengths of red or near-infrared light that penetrate the skin and are absorbed by the cells. This absorption stimulates the mitochondria, the energy powerhouses of our cells, to produce more ATP. ATP is the fuel that cells need to function optimally.
By increasing ATP production, Red Light Therapy promotes cellular repair, reduces inflammation, improves blood circulation, and supports the body's natural healing processes. It also activates signaling pathways that release nitric oxide and anti-inflammatory cytokines, further reducing inflammation and enhancing overall tissue health.
Red Light Therapy's specific wavelengths can penetrate deep into the skin, muscles, and joints, making it effective for various conditions. Its cellular-level effects help improve energy production, reduce inflammation, enhance circulation, and promote tissue rejuvenation.
In summary, Red Light Therapy utilizes specific wavelengths of light to stimulate cellular energy production and trigger beneficial biological responses, leading to improved healing, reduced inflammation, and enhanced overall well-being.
Understanding the Benefits of Red Light Therapy
Red light therapy offers a wide range of benefits, especially when incorporated before and after workouts. Let's explore three key benefits:
Red Light Therapy for Managing Joint Pain:
Red light therapy has shown promising results in reducing joint pain and inflammation. It can help alleviate discomfort caused by conditions such as arthritis or exercise-induced joint strain, allowing for improved mobility and pain management. The light penetrates deep into the joint tissues, promoting blood flow and reducing inflammation, which can help relieve pain and stiffness.
Red Light Therapy for Managing Muscle Pain:
Muscle soreness and fatigue are common after intense workouts. Red light therapy can aid in muscle recovery by reducing inflammation, increasing blood circulation, and promoting the repair of damaged muscle fibers. The light energy stimulates the production of collagen, which is essential for muscle tissue repair, helping to alleviate muscle soreness and accelerate recovery.
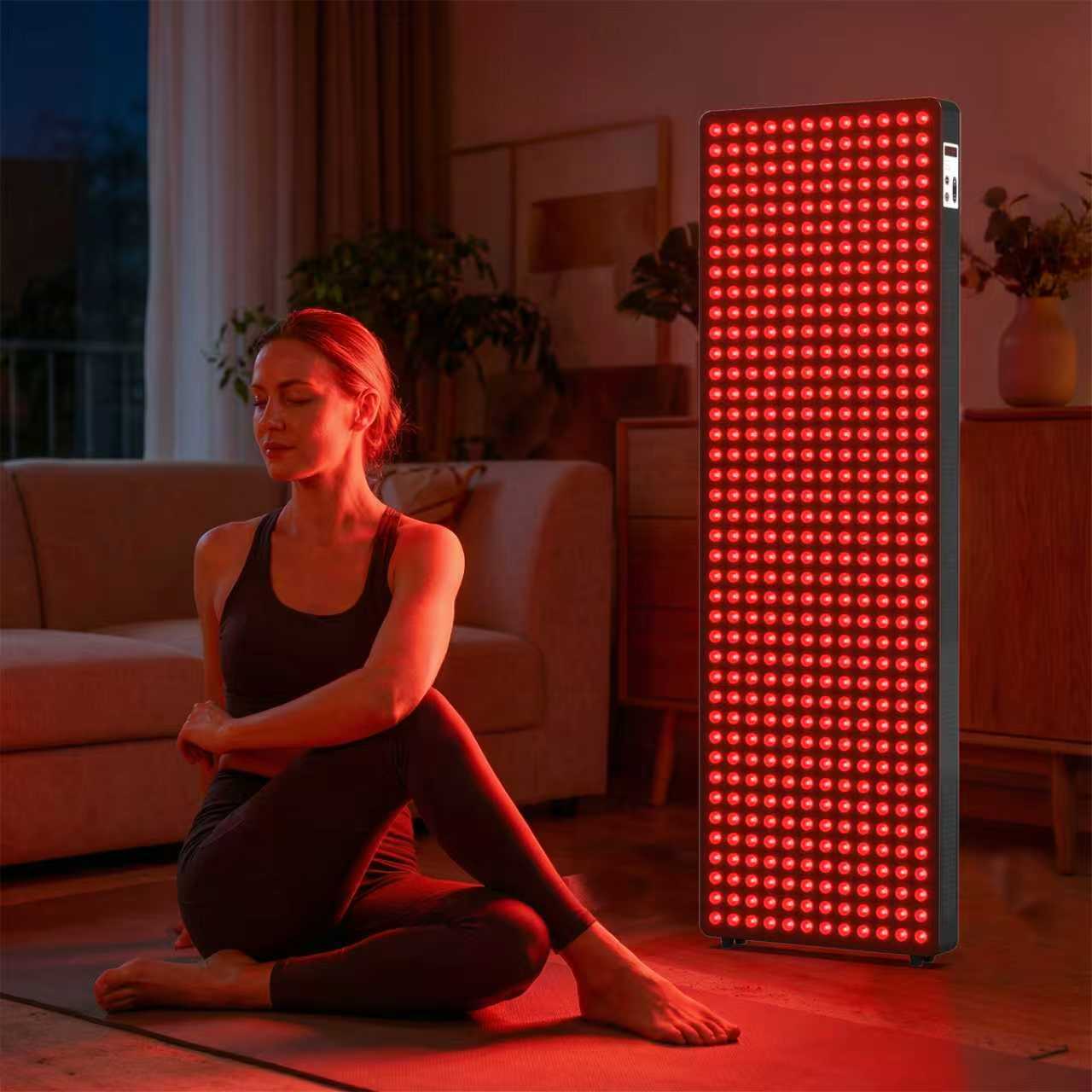
Red Light Therapy for Enhanced Post-Workout Recovery:
By stimulating cellular energy production, red light therapy accelerates the body's natural healing processes. It can speed up recovery time, reduce muscle fatigue, and enhance overall post-workout recovery, enabling you to bounce back faster for your next session. Additionally, red light therapy can improve sleep quality, which is crucial for recovery and muscle repair.
Best Practices: Using Red Light Therapy in Your Pre and Post-Workout Routine
To maximize the benefits of red light therapy, it's important to implement it correctly in your pre and post-workout routine. Here are some best practices to consider:
Pre-Workout:
Use red light therapy 30 minutes before your workout to increase blood flow, warm up the muscles, and enhance performance. Position the light therapy device at a suitable distance from the targeted area, ensuring proper coverage.
Focus the light on the specific areas you'll be targeting during your workout. For example, if you'll be doing leg exercises, direct the light towards your legs to enhance blood flow and prepare the muscles for activity.
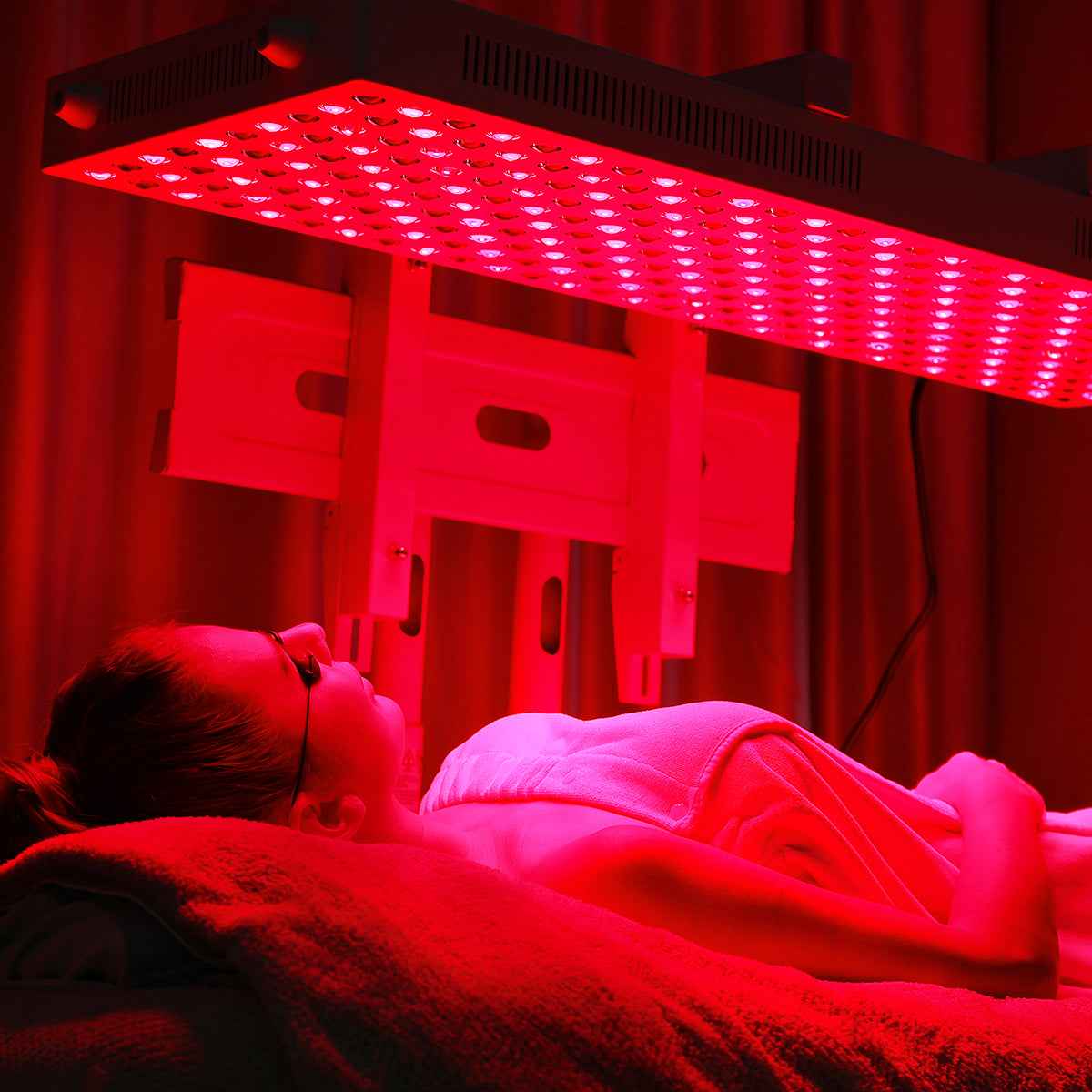
Post-Workout:
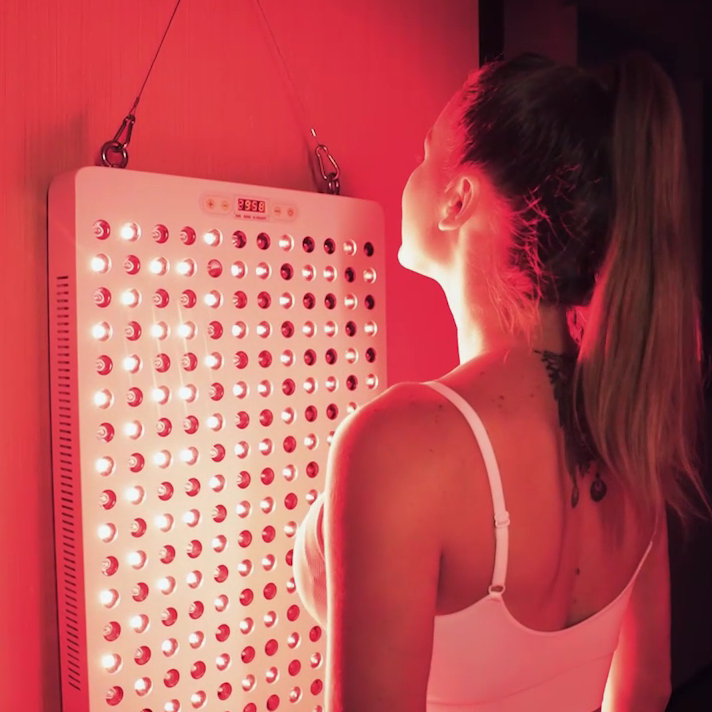
Apply red light therapy immediately after your workout to support muscle recovery and minimize post-exercise inflammation. Position the device to cover the muscles you have worked during the session.
Increase the duration of the therapy session to target all the muscles worked during the workout. Typically, a session of 10-20 minutes per targeted area is recommended.
Consider combining red light therapy with other recovery methods like stretching or foam rolling for comprehensive recovery benefits. This combination can further enhance muscle flexibility, reduce muscle tension, and promote overall relaxation.
Conclusion
Red light therapy is a powerful tool to incorporate into your pre and post-workout routine. Its ability to promote healing, reduce pain, and enhance recovery makes it a valuable addition to any fitness regimen. By following the best practices outlined in this guide, you can optimize the benefits of red light therapy and take your workouts to the next level. Remember to consult with a healthcare professional or a certified light therapy specialist to ensure proper usage and maximize the potential benefits of this therapy.













Leave a comment
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.